Is the Universe Expanding?
Abstract
For nearly a century, the expansion of the universe has been the cornerstone of the Big Bang theory. However, by late 2025, the conversation in cosmology has shifted from if the universe is expanding to how it is expanding—and whether that expansion is already beginning to fail. While the observation of galaxies moving away from one another (redshift) remains an empirical fact, new data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed that the rate of expansion is inconsistent and possibly slowing down.1 This article explores the current “Hubble Tension” and the emerging evidence of a potential transition from expansion to future contraction.
1. The Evidence: Why We Know Space is Stretching
The fundamental “fact” of expansion is built on the Doppler Effect applied to light. When we observe distant galaxies, their light is stretched into longer, redder wavelengths—a phenomenon known as redshift.
This recession is governed by the Hubble-Lemaître Law:
$$v = H_0 D$$
- $v$: The velocity at which a galaxy is moving away.
- $H_0$: The Hubble Constant (the expansion rate).2
- $D$: The distance of the galaxy from Earth.
By 2025, the JWST has refined these measurements to unprecedented levels, confirming that even after accounting for cosmic dust, distant galaxies are indeed moving away at speeds proportional to their distance [^1].
2. The 2025 “Hubble Tension” Crisis
Despite the confirmation of expansion, a massive discrepancy has emerged between two ways of measuring it:3
- Early Universe (CMB): Measurements of the “echo” of the Big Bang suggest an expansion rate of 67.4 km/s/Mpc.4
- Local Universe (Supernovae): Direct measurements of nearby stars and galaxies suggest a much faster rate of 73.0 km/s/Mpc [^2].5
This 8% difference, confirmed by JWST data in mid-2025, is now referred to as a “crisis in cosmology.”6 It suggests that either our measurements are flawed or—more likely—there is “new physics” such as evolving dark energy that we do not yet understand [^3].
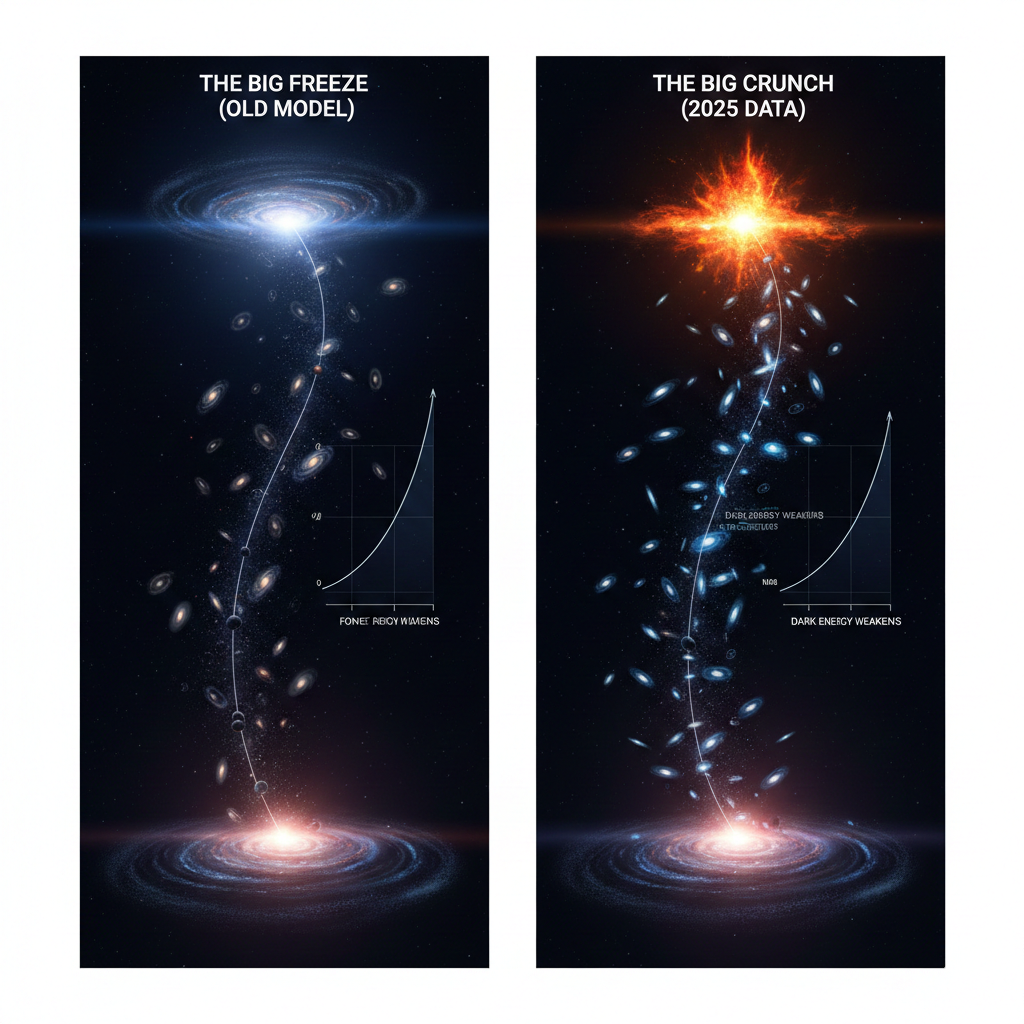
3. A Recent Twist: Is Expansion Slowing Down?
Historically, scientists believed the universe’s expansion was accelerating forever due to a “Cosmological Constant.” However, a groundbreaking study published in November 2025 in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society has challenged this [^4].7
The research utilized a new “age-bias” correction for Type Ia supernovae. The findings suggest that dark energy may not be a constant force but a weakening one.8 Remarkably, this data indicates that the universe may have already entered a decelerated expansion phase [^5].9
4. Conclusion: The Fate of the Cosmos
As of December 2025, the consensus is that the universe is currently expanding, but its long-term fate is no longer certain. If the recent findings of a “weakening” dark energy hold true, the universe could eventually reach a maximum size and then begin a multi-billion-year process of contraction, ending in a “Big Crunch”—a total collapse back into a singularity.10
Interesting Fact : Quran already mention 1400 years ago.
The Quran contains a specific verse that many modern scholars and scientists identify as an early reference to the expansion of the universe. In Surah Adh-Dhariyat (51:47), the text states: “And the heaven We constructed with strength, and indeed, We are [its] expander.” The Arabic word used is “musi’un,” which comes from the root wa-sa-’a, meaning to extend, widen, or make vast. While classical commentators originally interpreted this as a testament to God’s vast power or the immense size of the heavens, the active participle form implies an ongoing, continuous process of expansion—a concept that aligns remarkably with Edwin Hubble’s 20th-century discovery that galaxies are moving away from each other.
Beyond expansion, the Quran also touches upon the origin of the universe in a way that parallels the Big Bang theory. Surah Al-Anbiya (21:30) mentions that “the heavens and the earth were a joined entity, then We separated them.” This description of a “joined entity” (ratq) being “cloven asunder” (fataq) reflects the scientific model of a singularity expanding into the vast cosmos we see today. For many, these verses serve as a bridge between spiritual revelation and empirical science, suggesting that the dynamic nature of the universe was encoded in the text over 1,400 years ago.
Footnotes
[^1]: ESA – Webb & Hubble confirm Universe’s expansion rate (2025)
[^2]: NASA Science – The Hubble Constant and Hubble Tension (Updated 2025)
[^3]: Keck Observatory – Astronomers Sharpen the Universe’s Expansion Rate, Deepening a Cosmic Mystery (Dec 2025)
[^4]: Royal Astronomical Society – Universe’s expansion ‘is now slowing, not speeding up’ (Nov 2025)
[^5]: Smithsonian Magazine – The Universe’s Expansion May Be Slowing Down, New Research Suggests (Nov 2025)
Read other article : Iron is from the sky, not from earth. Bookmark this website for further important interesting articles.


