The Sun’s Fixed Course: Galactic Orbital Dynamics and the Architecture of Solar Motion
While the Sun appears to be the stationary heart of our planetary system, it is actually a high-speed voyager. Modern astrometry and gravitational physics have mapped the Sun’s movement, revealing that it does not drift aimlessly through the void. Instead, it adheres to a strictly defined orbit around the Galactic Center, governed by the mass distribution of the Milky Way.
1. The Geometry of the Galactic Orbit
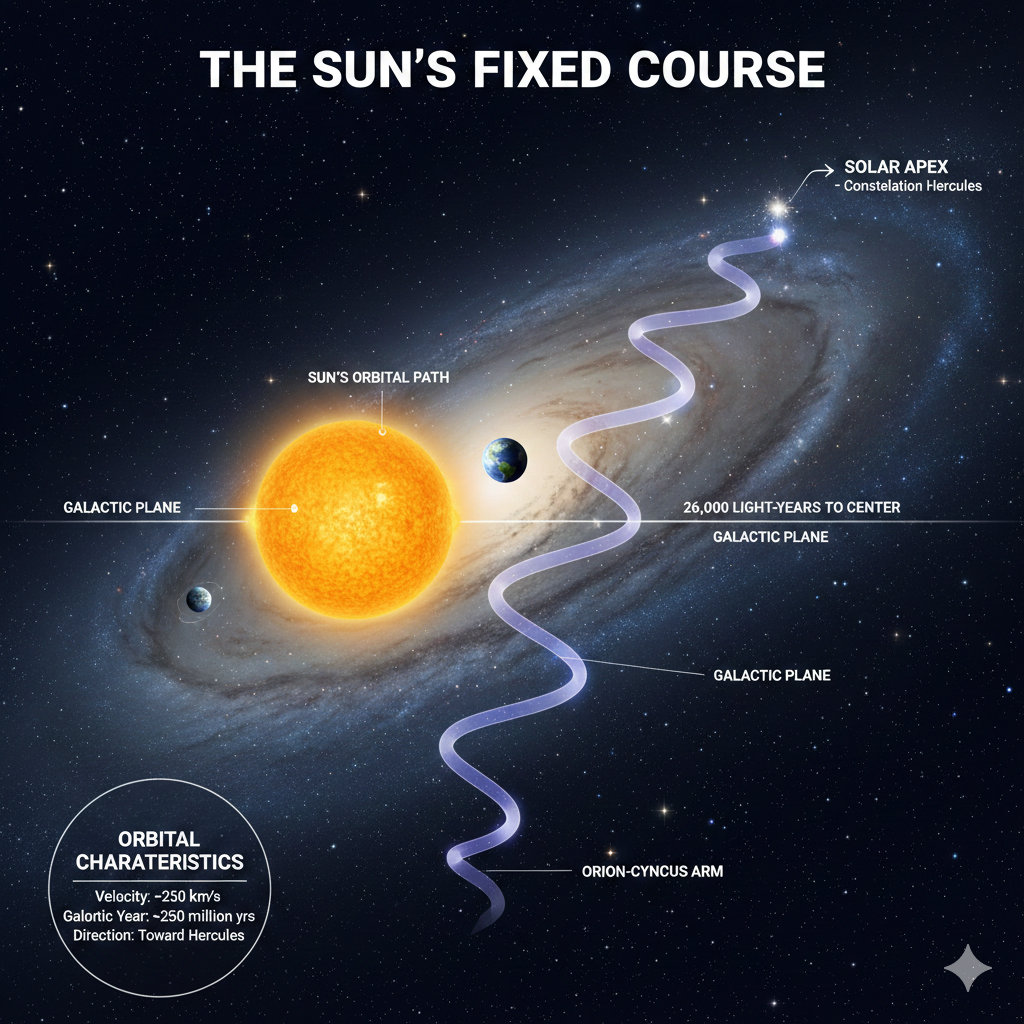
The Sun is situated in the Orion-Cygnus Arm, a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way. Our position is roughly 26,000 to 27,000 light-years from Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the galaxy’s core.
Rather than a simple circle, the Sun’s path is an elliptical orbit with low eccentricity. This path is dictated by the total gravitational potential of the galaxy, which includes the visible stars, the massive gas clouds, and the invisible “halo” of dark matter.
Velocity and the Galactic Year
The Sun travels at a staggering velocity of approximately 828,000 kilometers per hour ($230$ km/s). Even at this speed, the sheer scale of the Milky Way is so vast that it takes the Sun roughly 225 to 250 million years to complete one full revolution. This immense timeframe is known as a Galactic Year or Cosmic Year. To put this in perspective, the last time the Sun was in its current orbital position, the first dinosaurs were just beginning to appear on Earth [^1].
2. The Harmonic “Wobble”: Vertical Oscillation
The Sun’s “fixed course” is more complex than a flat ring. The Milky Way has a thin disk structure, and as the Sun orbits the center, it also moves vertically, “bobbing” up and down like a needle on a sewing machine.
- Gravitational Restoring Force: As the Sun moves above the galactic plane, the collective gravity of the stars and gas in the disk pulls it back down. As it passes through the plane and moves below it, the gravity pulls it back up again.
- The Sinusoidal Path: This creates a wave-like motion. The Sun crosses the central plane of the galaxy approximately every 30 to 32 million years.
- The Solar Apex: While this oscillation occurs, the Sun is continuously moving toward a specific point in space known as the Solar Apex, located near the constellation Hercules and the star Vega [^2].
3. Stability Within the Galactic Tide
The consistency of this path is vital for the stability of the solar system. Because the Sun moves in a predictable, “fixed” manner, the planets remain gravitationally bound to it without significant external disruption.
However, this path does lead us through different regions of space. As the Sun moves, it enters and exits various Interstellar Clouds—regions of differing gas density. Currently, we are moving through the “Local Fluff” (Local Interstellar Cloud), which is tempered by the Heliosphere, a magnetic shield generated by the Sun’s constant outward flow of solar wind [^3].
Comparison of Solar Motion Scales
| Scale of Motion | Reference Point | Velocity / Period |
| Planetary | Solar Barycenter | Earth orbits at ~$30$ km/s |
| Galactic Orbital | Galactic Center | Sun orbits at ~$230$ km/s |
| Vertical Oscillation | Galactic Plane | Crosses plane every ~$32$ million years |
| Local Motion | Local Standard of Rest | Sun moves at ~$20$ km/s relative to neighbors |
4. Conclusion: A Guided Trajectory
The Sun’s motion is a testament to the order of the cosmos. It is not a rogue star; it is a fundamental part of the galactic disk’s rotation. By studying the Solar Apex, the Galactic Year, and the Vertical Oscillation, astronomers can predict where our solar system has been and where it is going with remarkable mathematical precision [^4]. The sun moves in a defined orbit around the center of the Milky Way galaxy, following a consistent path rather than wandering aimlessly. And it is already mentioned in Quran Chapter 36. Verse 38. “And the sun runs on course toward its appointed term.”
Footnotes
Would you like me to expand on how this orbital path affects Earth’s climate over millions of years, or perhaps generate an image showing the Sun’s “corkscrew” motion through the galaxy?
[^1]:
NASA Science: Our Solar System’s Path – Deep dive into the Sun’s orbital period and galactic context.
[^2]:
The Astrophysical Journal: The Solar Motion – Academic papers detailing the calculation of the Solar Apex and Local Standard of Rest.
[^3]:
ESA: The Sun’s Journey Through the Galaxy – European Space Agency’s explanation of the heliosphere’s interaction with the interstellar medium.
[^4]:
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics: Galactic Dynamics – Resource on how gravitational mass dictates the “fixed” paths of stars.
Read other article The Universe is expanding